In the Analog and Digital tab, select the signals that you want to send in a message.
Tip |
|
|---|---|
|
If you define the output data in a virtual module and only enter here the references to these data, you can also include these data in the data recording as an option. |
|
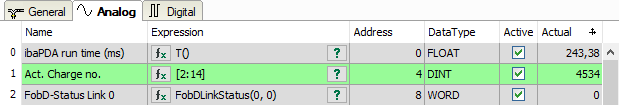
Analog and Digital tab
Other documentation |
|
|---|---|
|
For a description of the columns, please see the ibaPDA manual. |
|
Expression
In the Expression column, define the output signals in a similar way as the virtual signals. You can enter simple expressions or references to existing signals directly in the tables. You can also open the Expression editor via the <fx> button. You can analyze an incorrect expression via the <?> button.
Address
The address indicates the offset of the first byte of this value within the sent message. You can enter the offset as hexadecimal or decimal value by selecting the desired setting in the context menu.
The digital signals are addressed via the Address and Bit no. (0 – 15) columns.
DataType
ibaPDA supports the following data types: BYTE, WORD, DWORD, SINT, INT, DINT, FLOAT, DOUBLE, and STRING[32].
The address range depends on the data type. Hence, after changing the data type, you might have to adjust the address entries.
Active
For disabled signals, ibaPDA writes 0 in the telegram buffer.