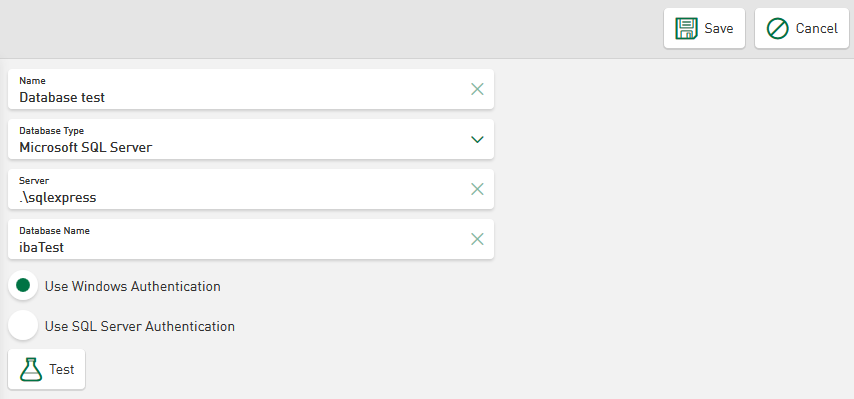
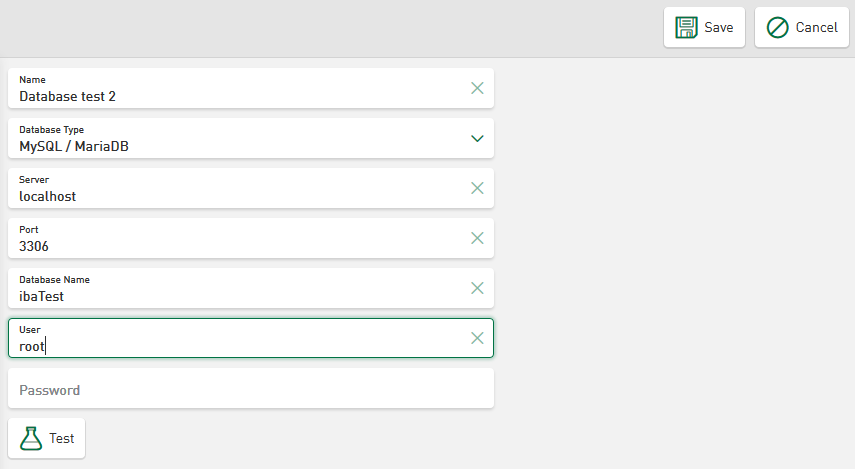
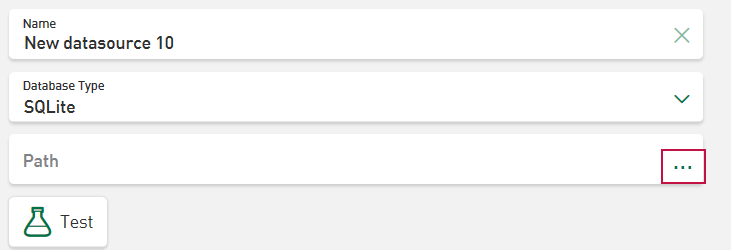
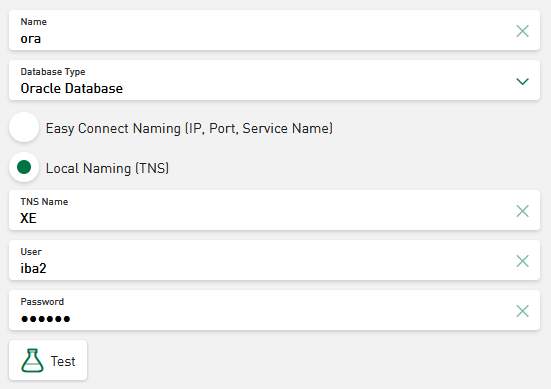
Depending on the database type, you have to make different entries. Examples of the following database types are shown below: Microsoft SQL, MySQL/MariaDB, SQLite and Oracle Database
Microsoft SQL connection
Windows authentication
The user account under which the ibaDaVIS service runs is used to connect to the MSSQL server instance. This is normally the system account. The user can also be changed to another user with administrator rights.
Note |
|
|---|---|
|
When using the local system account, the corresponding NT-AUTHORITY\SYSTEM login in the MSSQL server must be provided with additional permissions that are not set up by default. Required are the rights to connect to the database, to create and modify a table, and to write to a table. Clarify in advance with your DB administrator whether the extension of rights is possible or whether a different login or authentication should be selected. |
|
MySQL/MariaDB connection
SQLite connection
The storage destination of the SQLite file is specified in the field Path. Tap in the field to open the file selection dialog and simplify the specification of the SQLite database file. The search in the browser refers to the server-side system.