LimitAlarm('Expression','Limit','DeadBand','Time',' Reset=0’)
Arguments
|
'Expression' |
Measured value |
|
|
'Limit' |
Limit value, from which the function returns TRUE |
|
|
'DeadBand' |
Specification of a dead zone below the limit value, within which the function does not reset to FALSE |
|
|
'Time' |
Specification of the time, for which the measured value must be above the limit value until the function returns TRUE |
|
|
'Reset' |
Optional parameter (default = 0) to stop and restart the calculation |
|
|
'Reset' = 0 |
Perform calculation |
|
|
'Reset' = 1 |
Stop calculation, reset and set result to 0 |
|
|
'Reset' = 2 |
Stop calculation and keep result |
|
Description
This function monitors the measured value ('Expression') and sets the result to TRUE if the measured value is longer than the specified time ('Time') above the ('Limit') limit value. The result of the function becomes FALSE again if the measured value falls below the limit value by the value specified under the ('DeadBand') deadzone.
Tip |
|
|---|---|
|
The LimitAlarm function can also be used for a lower limit For this purpose, only the measured value and the limit value must be flipped, i.e. multiplied by (-1). e.g: LimitAlarm([0:1] *(-1), 9 *(-1), 0.5, 0.4) |
|
Example
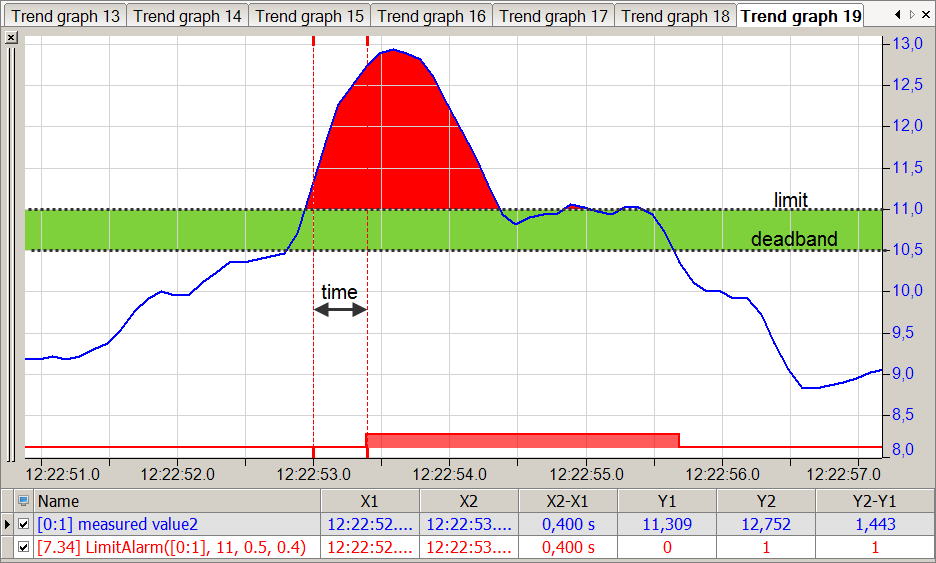
The function should return TRUE if the measured value is longer than 0.4 seconds above the value 11. The function should then return FALSE again if the measured value has fallen below 10.5.
Solution
In the figure below the blue curve shows the measured value and the red bar shows when the limit is exceeded. The green band shows the dead zone that prevents a direct FALSE setting of the function.