CountUpDown('Up','Down','Reset','UpperLimit=none','LowerLimit=none','ResetOnLimit=0')
Arguments
|
'Up' |
Digital signal whose rising edge (FALSE --> TRUE) increases the counter by 1 |
|
|
'Down' |
Digital signal whose falling edge (TRUE --> FALSE) decreases the counter by 1 |
|
|
'Reset' |
Optional parameter (default = 0) to stop, reset and restart the calculation |
|
|
'Reset' = 0 |
Perform calculation |
|
|
'Reset' = 1 |
Stop calculation and set result to 0 |
|
|
'UpperLimit' |
Optional parameter (default = 0); upper limit for counter value |
|
|
'LowerLimit' |
Optional parameter (default = 0); lower limit for counter value |
|
|
'ResetOnLimit' |
Optional parameter (default = 0) for resetting the counter value when reaching a limit |
|
|
'ResetOnLimit'= 0 |
Counter value stays on limit value after reaching a limit |
|
|
'ResetOnLimit' = 1 |
Counter value is reset to 0 after reaching a limit |
|
Description
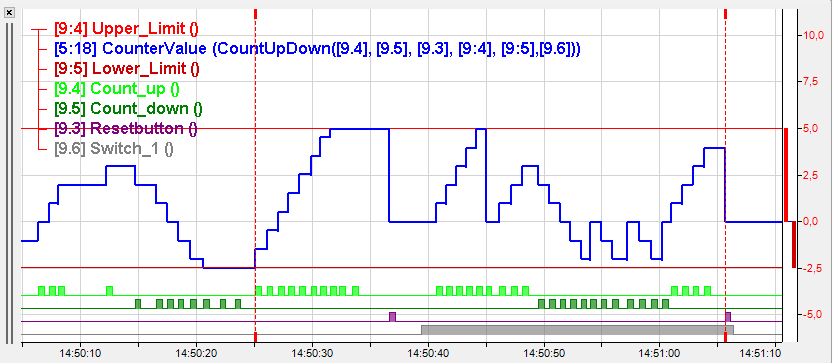
This function generates a counter value which is increased by 1 with every rising edge on 'Up' and decreased by 1 with every rising edge on 'Down'. Counting is not limited but can be reset to zero with 'Reset' = TRUE or 1.
'UpperLimit' and 'LowerLimit' are optional and can be specified either by a fix value or an expression. If limit arguments are specified and the counter reaches a limit, it does not continue counting but stays on the limit value until either a counter pulse in the other direction occurs or 'Reset' is set to TRUE.
If the optional parameter 'ResetOnLimit' is TRUE or 1, then the counter will be reset to zero as soon as it reaches or exceeds a limit.
Resetting to zero only works if the lower limit is <0 and the upper limit is >0.
Example