This section describes the configuration of the latest generation of ibaFOB cards, the ibaFOB-D interface card. An FOB (fiber optical board) is an interface card for fiber optical connections.
It applies to all versions of the card, such as ibaFOB-io-D, ibaFOB-2io-D and ibaFOB-4io-D (FOB4i-D + FOB-4o-D), as well as to PCI and PCIe types. ibaFOB-…-Dexp is the PCI Express variant of the card.
Beside the new 32 Mbit flex protocol, the generation of ibaFOB-D cards can also process all previous ibaNet data transfer rates and modes of measurement.
These descriptions generally also apply to previous card generations such as -PCI, -S and -X. Some functions, however, could have been removed, replaced or added. Furthermore, previous cards had only limited options regarding data transfer rate and modes of measurements.
All modules that may previously have been assigned in ibaPDA to ibaFOB-F, ibaFOB-S and ibaFOB-X cards, can also be assigned to an ibaFOB-D card / ibaFOB-Dexp card.
The system automatically detects which card(s) are installed and shows them in the tree structure. You may use cards of different generations simultaneously in the same computer. You will see different names in the tree structure depending on the card model installed.
Cards with output channels ("…io…") or with an output module ("ibaFOB-4o…") can be used to emit signals from ibaPDA. The card then also appears in the tree structure in the outputs area of the I/O Manager. Suitable modules for the outputs can then be added there.
For more information see Outputs.
Notes |
|
|---|---|
|
|
Other documentation |
|
|---|---|
|
For more information about the hardware features of the cards, see the relevant manual for the respective card. Information on previous ibaFOB-io cards can be found in the corresponding card manual or in previous editions of the ibaPDA manual. |
|
If you select the ibaFOB-…-D interface in the tree structure of the ibaPDA I/O Manager, then a simple presentation of the card is displayed in the Configuration tab in the right part of the dialog.
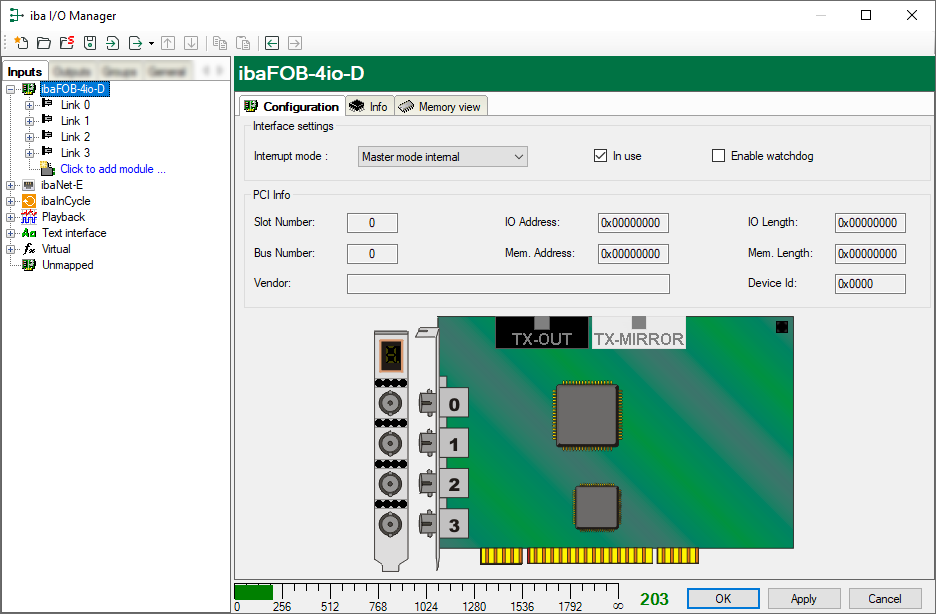
The dialog window provides you with the information described in the following chapters.