What does PTP mean?
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a communications protocol for synchronizing the system time of different systems (PC, PLC and other devices) in a network. The protocol is defined in accordance with Standard IEEE 1588.
In a typical PTP topology, there is one time master and one or more time slaves that synchronize to the master. The highest synchronization accuracy of software-based PTP applications, as in ibaPDA, is 5 ms.
ibaPDA can be configured as slave. When an ibaPDA system is configured as a time slave, it synchronizes to a time master in the network, provided one is available.
ibaPDA supports the standard PTPv2 according to IEEE 1588-2008 (or "IEEE 1588-V2"). With the new process, only the multicast address 224.0.1.129 is used in all domains to distribute the time in the network. The domain number can have the value 0 to 255 and is part of the time telegram.
PTP settings, time slave
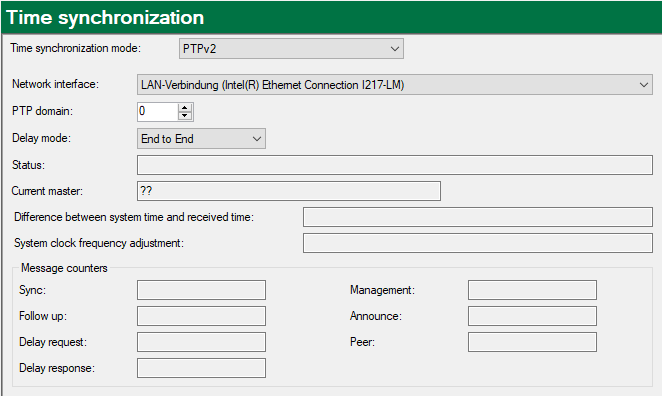
Network interface
Here, choose the network interface of the ibaPDA computer to be used for time synchronization.
PTP domain
If ibaPDA is configured as a slave, set the same PTP domain on which the time master is also sending.
If ibaPDA is configured as a master, you can set any PTP domain between 0 and 255.
Delay mode
The accuracy of the PTP protocol is based on the continuous computation of delays which can occur at any time when transmitting information in a network and taking these delays into account for the time synchronization of the time slaves. You can choose between two methods which are available for this purpose.
-
End-to-End: This method determines the delay between time master and time slave over the entire way through the network. Therefore, the slave sends a "Delay request" message to the master, which in return responds with a "Delay response" message. This is used to calculate the transit time of the message through the network. The method is suitable for any network even if network components such as switches, hubs or routers are not necessarily PTP-compliant. However, the achievable accuracy of the end-to-end method in a network is lower than the accuracy of the peer-to-peer method in a network of the same topology and with "PTP-transparent clocks" Moreover, the end-to-end method generates a higher network load, particularly if multiple slaves are in the network.
-
Peer-to-Peer: This method calculates the delay between the ports of adjacent devices by means of so called "Peer-delay-request/-response" messages. All network devices along the way between time master and time slave determine the delay on the section towards the devices they are directly connected with and pass on this information to the next device. The total delay between master and slave is calculated by so called PTP-transparent clocks (switch, hub or router) by writing the received delay value - supplemented with the delay which may be generated by the device itself - into the correction field of a PTP event message (e.g. sync telegram). The peer-to-peer method applies only to networks which are fully PTP-compliant. It generates less network load and it is less sensitive regarding asymmetries or changes in the network compared to the end-to-end method.
Status
The status field shows the current status of the time synchronization. The time synchronization only works when the acquisition is running.
Current master
If ibaPDA is configured as a slave, the IP address of the time master is shown here for information purposes.
Difference between system time and received time
The received time is cyclically compared with the system time whereas deviation is determined. Depending on whether the difference is rather positive or rather negative, a corresponding frequency adjustment of the internal system clock is calculated.
System clock frequency adjustment
The value of the frequency adjustment has been determined from the difference between the system time and the received time. Thus, a system clock which is too fast or too slow is corrected.
Message counters
This overview shows different message counters. There is one counter per telegram type. If there is a master-slave connection, the counters usually count up: sync, announce, delay request and delay response.