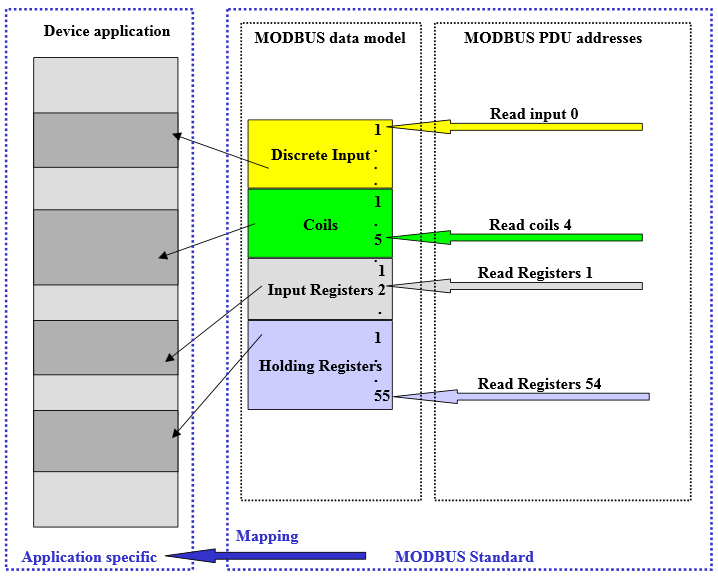
The 4 data types are stored in different, possibly even overlapping storage areas. The accesses to the physical storage address are mapped by means of the application on the Modbus server.
Basically, Modbus distinguishes between the internal numbering (Discrete Inputs, Coils, Register), which usually begins with 1 and the addressing of the objects, usually beginning with 0.
Example: On many Modbus servers, the basic types are mapped in the following address spaces:
|
Coils |
0x00000 |
|
Inputs |
0x10000 |
|
Input Registers |
0x30000 |
|
Holding Registers |
0x40000 |
This means, that the Holding register 1 is stored on the address 0x40000. The Holding register 1 is accessed by the logical reference number (address) 0. The input register 1 is stored on the address 0x30000. The input register 1 is also accessed by the address 0.
The logical Modbus reference numbers that are used for Modbus functions are integer indices without sign and beginning with 0.