The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the core protocols of the Internet protocol suite.
IP handles lower-level transmissions from computer to computer as a message makes its way across the Internet. TCP operates at a higher level (transport level), concerned with the two end systems. TCP provides a reliable data stream of bytes from a program on one computer to another program on another computer. TCP is explained in RFC1180 and in RFC793 (see References).
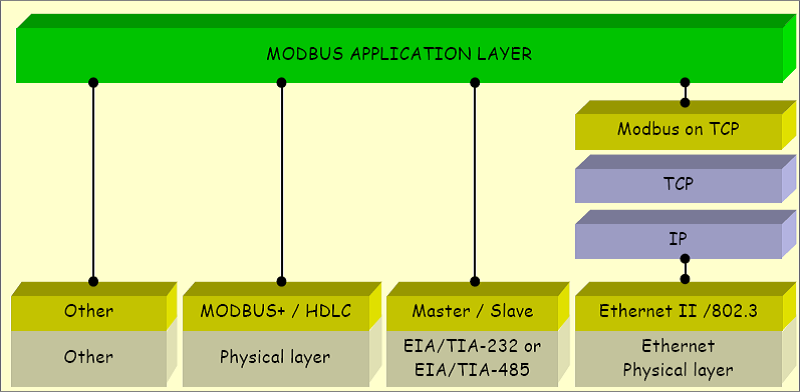
Modbus is a protocol for the client/server communication between devices connected on different types of buses or networks.
Modbus is currently implemented in the following buses or networks as shown in the following figure:
-
-
TCP/IP over Ethernet
-
Asynchronous serial transmission over a variety of media
-
Modbus PLUS (a high speed communication via a token passing network)
-
ibaPDA has the possibility to measure signals via the Modbus protocol over serial connections (Modbus ASCII and Modbus RTU) and over TCP/IP. This manual describes the connection via TCP/IP and as variant the transmission of the Modbus RTU protocol over TCP/IP, with ibaPDA acting as client.
All systems that can receive and respond to messages with the Modbus-TCP protocol as server, can also communicate with ibaPDA.